-
Posts
8,051 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Articles
Everything posted by kye
-
This is awesome - thanks for sharing! What kind of DCTLs are you writing?
-
Doh - forgot to list the 9mm F1.7 lens. That's the ultra-wide I'll be taking too. So the total count is one body, 5 lenses, my phone with vND. I was slightly conflicted about the "wide-angle night cinema" slot. The SB+50/1.4 is equivalent to a 71mm F2.0 on FF, so having something wider seems an obvious thing but I'm just not sure if I would use it. I've mentioned the 12-35mm F2.8 as my night walk-around lens, and when combined with the GH7 low-light capability it's a fine combination, but it's not crazy fast/bright and isn't the best "cinema" option around. The things I considered were: my TTartsans 17mm F1.4, which is small and light and despite being soft wide-open is probably quite cinematic my 14mm F2.5 which is small and light but is bettered by the 12-35mm on flexibility grounds being a zoom my Voigtlander 17.5mm F0.95, which is a great performer but is quite heavy my c-mount 12.5mm F1.9, which is similar FOV when you crop in to its S16 image circle my 9mm F1.7 combined with the GH7 cropping, which is fast but sacrifices resolution and doesn't have the DOF advantages of other options (although I am already taking it) SB + 28mm F2.8 combos, but it's hard to get a reasonable quality 28mm F2.8 in M42 mount and it's not that fast anyway I opted to take the 12-35mm (which I sort-of take as a backup lens to the 14-140mm zoom) but if I do end up wanting a wider fast lens for night cinema, I think I might just bite the bullet and get the PanaLeica 15mm F1.7 as it'll be light and have AF and be sharper than I could ever want. I looked at the reviews of a bunch of budget F1.4 or faster lenses around the 14-20mm mark but I'd never be sure if it was as sharp as I'd like, and spending money to get something that isn't that much faster than my 17/1.4 or that much lighter than my 17.5/0.95 seems silly. MFT is the wrong format for ultra-fast wide lenses, and I already have lots of options for something I might not use, so the whole thing might end up being academic anyway.
-
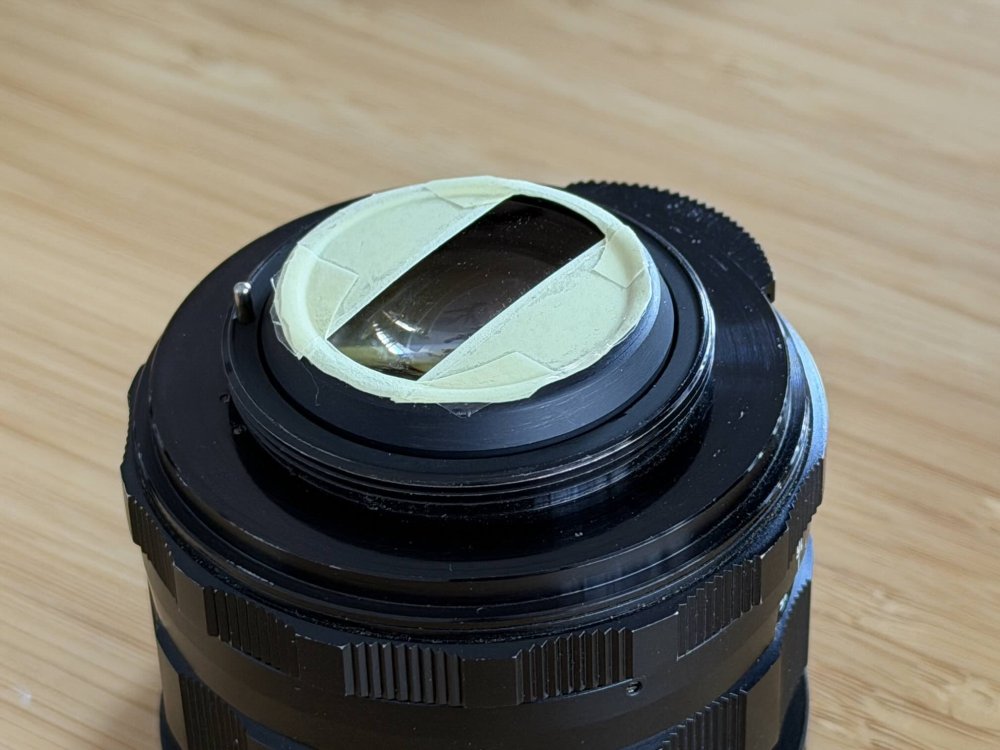
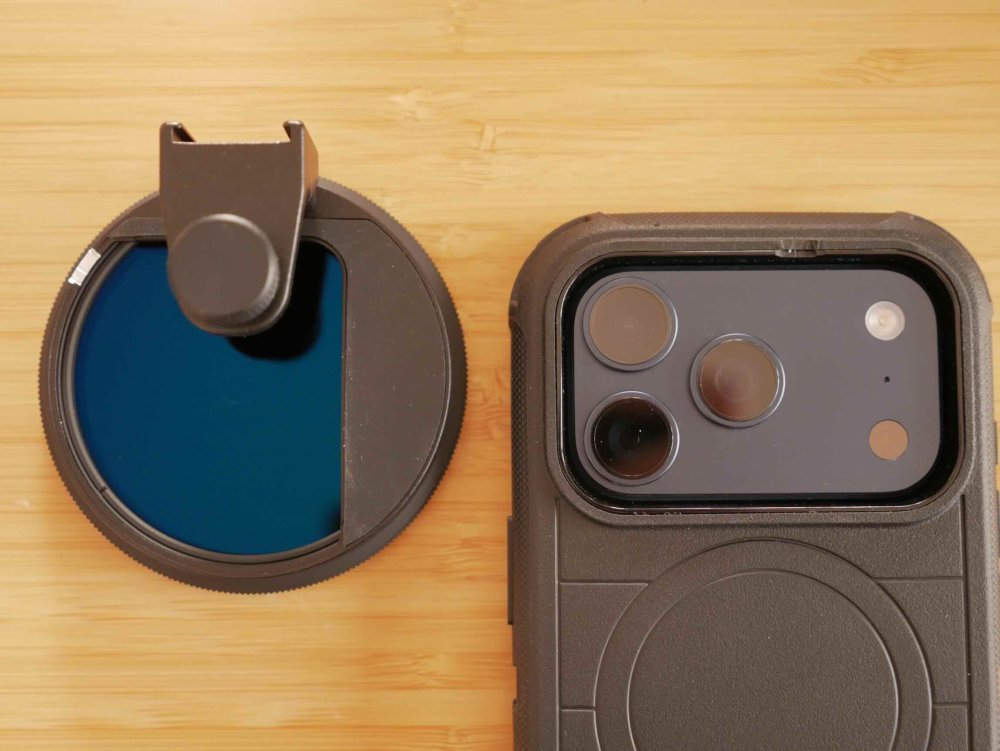
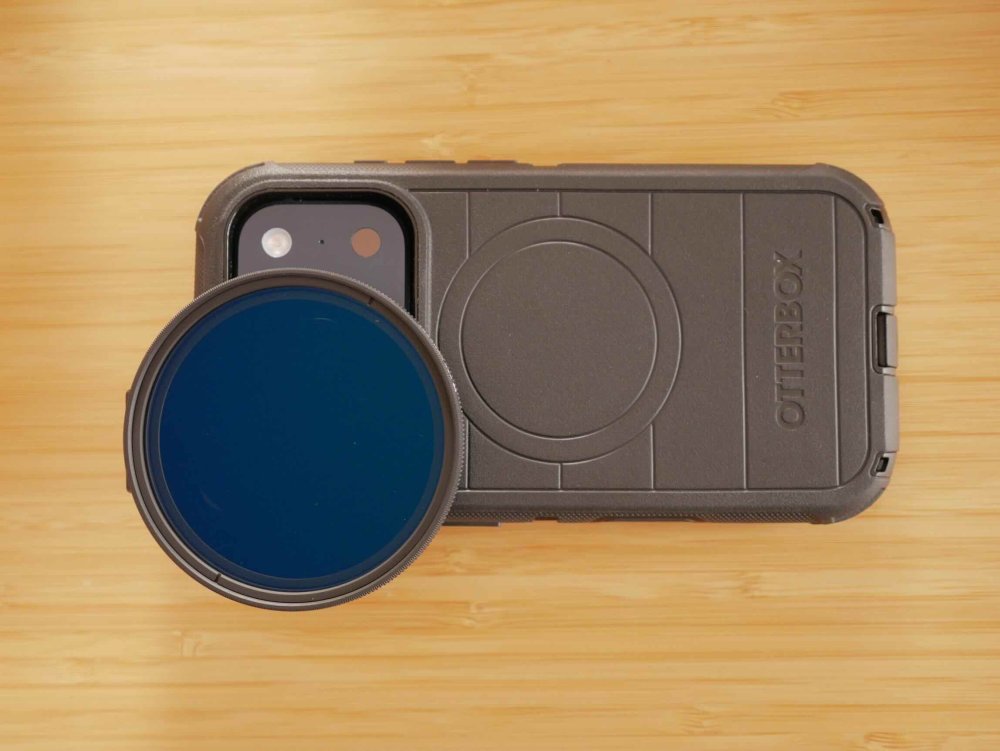
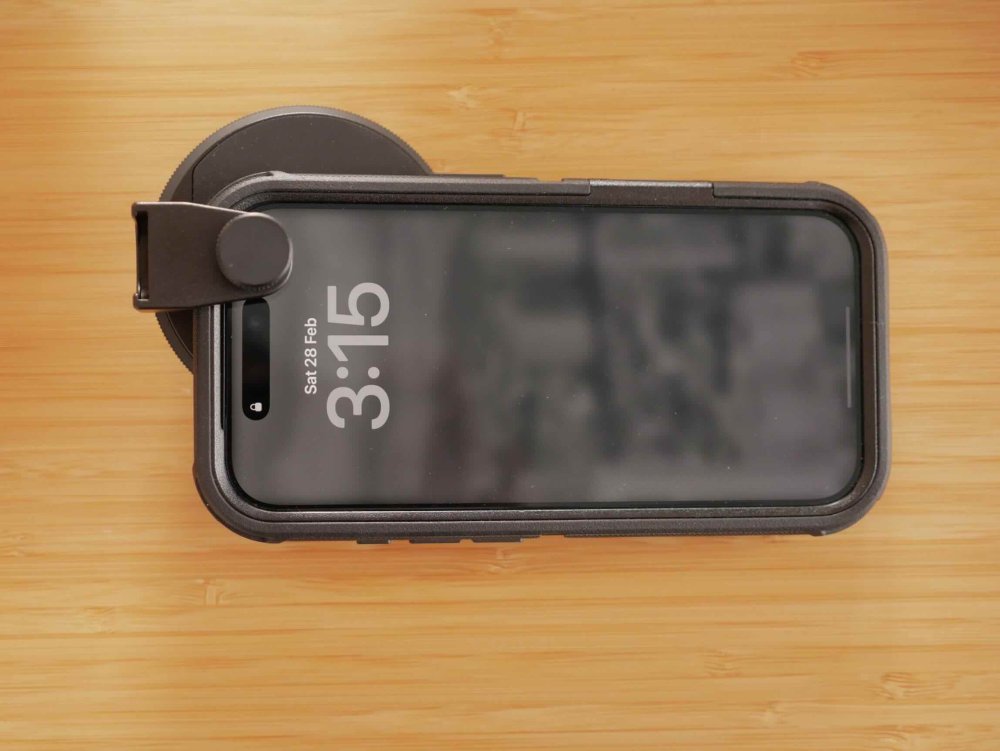
Getting prepped for my next trip and have further refined my setup. This trip is a quick trip to China, but it's also a test case for a trip I'm taking later in the year to Europe where the packing approach will be minimalism. Unlike the way I like to travel in Asia, the Europe trip will involve changing accommodation every few days, so packing and unpacking and hauling bags around will be much more of a pain, so I'll try and travel really minimally. As such, my approach for this trip is "when in doubt, don't take it" and see what I actually use. So the setup for this trip is: GH7 14-140mm F3.5-5.6 zoom, which I use during the day at F5.6 which means my 1-5 stop vND is enough 12-35mm F2.8 zoom, which is a great walk-around lens after dark Takumar 50mm F1.4 with M42-MFT Speedbooster (with bokeh insert) for "night cinema" iPhone 17 Pro setup (Neewer phone filter mount, K&F 1-9 stop vND, MagSafe Popsocket) The GH7 and zooms are self-explanatory, so here's the 50mm F1.4 setup. I have played around with "inserts" and ended up with a pretty extreme design, so this is a test to see if the vertical edges are too strong a look for me. It's made from the sticky part of the post-it note, and a layer of sticky tape over the top to keep it a bit more together. It sits between the speed booster and the lens, and I won't use the speed booster for any other lenses while travelling so this will stay in there and protected, so doesn't need to be that robust. It's a strong look in some situations and quite "painterly" in others, so I'll be curious how it goes. For my iPhone 17 Pro, it's a phone most of the time and a camera only as a backup, so I searched for a setup that would: Protect my phone from drops (I dropped it on the last trip and the screen shattered, despite it being in an Apple case - the only one available at the time... sigh) Still be right-sized for getting in and out of pockets etc Have a vND solution for when I want to shoot and use 180 shutter I'll spare everyone from the rant about the options out there (everyone wants you to buy into their "ecosystem" now) so I ended up with the Otterbox Defender Series Pro case, which makes the iPhone feel even larger than it did in the Apple case (which doesn't seem possible but is true), but seems very robust. The vND is the Neewer phone filter mount, which sort-of clips onto the phone (It's designed to screw onto and clamp the phone but you're clamping against the screen, so I wouldn't tighten it that much). It's designed for a naked iPhone, so I had to modify it (and the Otterbox case) slightly where it interfered with the Otterbox case to get it to sit a bit flatter. It still doesn't sit flush, but it goes on and seems to be fine. I haven't got around to actually taking it out to shoot with it, so that remains to be seen. I paired it with the K&F 1-9 stop vND, which boasts 18 layers etc, but doesn't claim to be a "True Colour" one like the 1-5 stop ones do. It doesn't have hard stops and I think it still gives the X at the max amount, but I'll see how I go. Not having an aperture sure sucks considering you're not really losing having shallow DOF. That is all combined with the MagSafe Popsocket as a safeguard. I've used the adhesive popsockets before and they're great for giving a much better grip on the phone, but I wasn't sure how strongly the MagSafe would be. The Otterbox claims to have magnets in it that strengthen the MagSafe connection, and this might be true. It feels quite sturdy actually, and I tested it to require 1.75kg of force to pull off, compared to the 1.45kg of force it took to pull it off my naked iPhone 12 mini. No idea what strength a naked iPhone 17 Pro MagSafe connection would have, but it's not terrible. Lots of compromises involved, but it's really my backup camera, and the Otterbox case is very grippy, so I'll see how I go.
-
Come on John... everyone knows that anyone who wants better footage than a smartphone can provide is 100% totally fine with a camera the size of a microwave oven that looks like a Borg prototype! Being slightly serious though, it's easy to criticise, but as someone who wants flexibility and better sound options, this is FAR better than the previous options, so it's a welcome addition in my eyes. The worst enemy of progress is criticising everything that isn't perfect in every conceivable way.
-
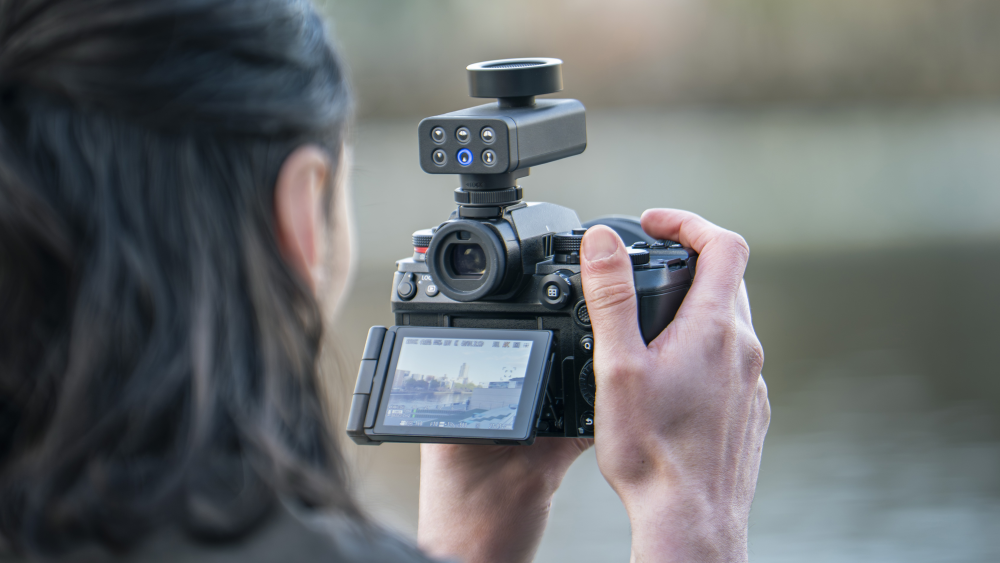
Panasonic just released a new on-camera mic. Looks like an excellent option for events etc where you want something small or something really flexible. I've watched a few YT showcases and for me, the best features are: It gives you 32-bit without having to have the external mic preamp box (and then adding microphones to that, making it larger again) It's small, much smaller than an on-camera shotgun mic You can quickly swap between modes (I assume?) it's powered by the camera It unlocks the ability to record >2 channels of audio into the files (one person said you can record left/right/mono/mono-20dB as a combo, and left/right/left-20dB/right-20dB as a different combo) It's definitely not magic and the laws of physics still apply. There don't seem to be any really good on-location stress tests posted yet, but there's a few examples. Media Division did an in-kitchen test to compare it to in-camera mics and lav and a DJI clip-on, and also applied a bit of AI voice isolation too to see how far you can push it: Dustin did some good tests including walking a 360 around the camera in each mode, which showed how directional it is, which seems pretty impressive. He also compared it to the Sennheiser MKE440. This shows the different modes out in nature: This is probably a complete revolution for a number of niche uses. Content creators would be one, where they're recording in noisy environments but still staying relatively close to the camera where physics will be helping them. Another is where the flexibility really helps, like shooting events where getting pristine audio isn't an absolute must but working super-quickly is more important and perhaps the 32-bit would really come into its own. This reminds me of how people used to talk about Panasonic when the GH4 and GH5 were around and people were saying that Panasonic just listened to people and then implemented the features that people would use rather than trying to be flashy and grab headlines. This will be an invisible workhorse for lots and lots of people.
-
Nice! What formats and focal lengths is it compatible with? and what camera and taking lens combos are you planning to use with it?
-
My take on the situation is that I'm super-happy with the GH7. It basically does everything I want, and apart from having ultra-sharp ultra-shallow DOF, pretty much does most things that FF does. It does low-light very well, and is only behind the low-light from FF cameras because they have gotten crazy good.
-
I went with the GH7 as I'm video-first and need the heat management etc. The G9ii is an incredible camera though. There's a whole thread about it here: https://www.eoshd.com/comments/topic/90374-panasonic-g9-mark-ii-i-was-wrong/ Do you have either one?
-
It was released in mid-2024 🙂 Definitely a strong camera though. I expect mine to be useful for many years, and TBH, I haven't felt jealous over a new camera release since buying it.
-
For anyone interested in understanding a bit more about the relationship between technical measurements and aesthetic experiences, this video is very interesting. Perhaps the challenge is that many people believe there's a golden zone of sharpness where it's softer than clinical glass, but sharper than poor performance vintage glass, but as there's very little qualitative data it's hard to know how a lens performs. The video gives a non-technical primer on MTF charts, and discusses what potential uses there are for different levels of performance, culminating in this chart. I particularly like this approach because the thinking is well beyond "good vs bad" lenses and takes the much more mature approach of "the right tool for the job". This is an example of this kind of thinking from the video: Recommended viewing if you want to go beyond "I like this lens" and "I don't like that lens"!
-
I find it incredible that people talk about switching bodies / systems all the time without really considering the wider ecosystem of lenses and accessories. Hell, I've stayed within the MFT system and whenever I get a new MFT body there are still all these extras that I end up being surprised about and inflate the price by 10-15%. If I was re-buying lenses then it would double/triple/quadruple the cost. I have no idea what the economics of lenses are, but I wouldn't be surprised if the camera body is now a loss-leader and the lenses where all the profit is.
-
Well, we've gotten drastically better pixels, but because everyone has been screaming incoherently about wanting sharper images the manufacturers took the higher performance and kept the same overall image performance but made the pixels smaller so there's more of them. Everyone said they wanted a camera that could match the 2.5K Alexa, but because there were more people screaming for resolution than screaming for quality the industry took it's improvements and gave us mediocre 4K cameras, then more improvements and we got good but not great 5K downsampling cameras, then more improvements and we got quite good 6K cameras, and since then the flagship bodies have given us 8K / 12K / 17K cameras with pixels that are close to rivalling the 2.5K Alexa. So ARRI released the Alexa 35, and now there's a 4K ARRI camera that absolutely smashes the 8K / 12K / 17K flagship cameras. It's a complete myth that cameras aren't getting better. They're getting better by leaps and bounds, but almost all those gains have been "spent" on smaller pixels / higher resolution. If that hadn't been the case, you'd probably have had every other feature you've ever wanted by now.
-
Good points. The way I see it is there's a toxic feedback loop of consumerism, hype, marketing, and release cycles. The skepticism and criticisms around this is justified, but the forgotten ingredient in this whole picture is us - the people paying attention. Without us, the whole thing falls flat. I would suggest the uncomfortable truth is that the people caught up in the drama of it are either making money from it (manufacturers, dealers, influencers, etc) or are desperately trying to buy their way into making nicer images. I will be the first to admit I did this. I tried to buy gorgeous images by swallowing the myth that Canon colour science was the answer, then that 4K was the answer, then that shallow DOF was the answer. The truth was that even if someone handed me an Alexa LF I'd still have made awful looking images. Sure, there are people making great work and want to upgrade their equipment from time to time and dip into the chaos briefly, but once they've made their decision and bought something that works for them, they tune out again. These people are spending their time on lighting tutorials, getting better at pre-production and planning, learning how to improve their edits, etc. They're not watching reviews and talking online about the colour subsampling of the 120p modes of the latest 12 cameras that are rumoured to come out in the next 17 minutes. My advice to you is this - if you feel like this then take a break from the industry and try and remember why you got into this in the first place. I'll bet it wasn't because you found a deep love for reading spec sheets!
-
"my mood tanks and it bleeds into the set" is a great way to express what I was thinking. I might have to steal your wording! I've had cameras I've loved to use and ones I always felt like I was struggling against, and it's definitely something that can be difficult to quantify. I suspect it's that we each have a range of priorities and preferences, and after getting used to the equipment and learning how it impacts the whole pipeline from planning through delivery and perhaps even into repeat business, the feeling we get is perhaps representative of how well it aligns with our individual preferences. It's easy to compare specs and pixel pee images, but there are lots of things that can be a complete PITA that don't show up on the brochures or technical tests. When reading your original post it felt like you want to go with the C50 and are trying to talk yourself into it / justify it. One thing that I think is underrated is the idea of the quiet workhorse. A camera that is a professional tool, does what you need without fuss, and doesn't have a lot of fanfare. For me that was the GH5 (although the colour science and AF weren't great) and now the GH7. These sorts of cameras don't grab headlines, but the fact that they're quiet workhorses rather than outlandish divas means you're able to move past the tech and concentrate on what you're shooting and the quality of the work. Canon have a very solid reputation in this regard - there's a reason they ruled the doc space for decades. One other thought.. if you don't have one already, consider buying a nice matte box. It'll help to stabilise the rig and will also make you look more impressive to clients!
-
I think you've been looking at the camera industry too long. We operate in a marketplace where people offer goods and services and if people want to purchase them they do, and if not, they don't. There are reasons why Governments might incentivise or subsidise various industries or products or behaviours, but I don't think any of these apply to cameras. The only other situation that is an exception is if something starts to become a necessity, like clean water or reliable electricity supply, and more recently now internet access is getting into this territory. When this happens then efforts might need to be made to ensure that these things are accessible. I very much doubt anyone is arguing that high-end mirrorless cameras are a human right, in which case they should just be traded like all goods, where they're subject to the laws of demand and supply. You can't get your house painted for $50 because paint and labour costs more than that. You can't buy a car for $9 because no-one has worked out how to make them for anything remotely like that price. You can't buy a super-car for $10000 because the market has valued them significantly above that.
-
Two thoughts from me. If you close your eyes and imagine each scenario, how do each of them make you feel? What is never really talked about is that if you feel like you're having to argue or strong-arm your equipment then you'll be in a bad mood, which isn't conducive to a happy set, getting good creative outputs, or just enjoying your life. I think people dismiss this, but if you're directing the talent then this can really matter - people can tell if you're in a good mood or distracted or frustrated etc and people tend to take things personally so your frustrations with the rig can just as easily be interpreted by others that you're not happy with their efforts. The odd little image technical niggle here or there won't make nearly as much difference as enjoying what you do vs not. When it comes to IBIS vs Giroflow vs EIS etc, it's worth questioning if more stabilisation is better. For the "very dynamic handheld shots" having a bit more camera motion might even be a good thing if it is the right kind of motion. Big budget productions have chosen to run with shoulder-mounted large camera rigs and the camera shake was pleasing and added to the energy of the scene. Small amounts of camera shake can be aesthetically awful if they're the artefacts from inadequate OIS + IBIS + EIS stabilisation, whereas much more significant amounts of camera shake can be aesthetically benign if coming from a heavier rig without IBIS or OIS. If more stabilisation is better, maybe it would be better overall to have a physical solution that can be used for those shots? Even if there aren't good options for those things, maybe the results would be better if those shots were just avoided somehow? In todays age of social media and shorts etc, having large camera moves that are completely stable is basically a special effect, and maybe there are other special effects that can be done in post that are just as effective but are much easier to shoot?
-
Good to hear you got a solution that works for your (very challenging) shooting requirements - that's what truly matters! Low-light is now the current limitation for the high-end MFT line-up. The GH7 sacrifices having a dual-base-ISO in favour of having the dual-readouts and the DR boost that architecture gives. I shoot uncontrolled external locations in available light, which means low-light performance is a consideration for me too, but the GH7s performance is enough for my needs. I suspect the low-light capabilities of MFT would be described as "Very Good to Excellent", but the latest FF cameras now have low-light capabilities that would be described as "Absolutely Incredible" and so MFT lags by comparison. You can't cheat the laws of physics! It wasn't that long ago that cameras weren't really usable above ISO 1600 or 3200, so things have advanced very quickly. Suggesting that you "need" to shooting weddings at ISO 25,600 would have been considered a joke and saying you were serious would have started arguments and gotten you banned as a troll! Personally I think the "if todays cameras can't do it then you don't need it" is a silly perspective, because it implies that there aren't any new situations or circumstances that are worth recording, and obviously that's just plain ridiculous. I wonder how the GH7 compares to the original A7S. The difference might be smaller than you'd think.
-

Where did Mattias Burling go? Youtube channel is gone.
kye replied to John Matthews's topic in Cameras
I remember a quote from around the time that Facebook started having issues with people passing away - "in 80 years there will be 800 million dead people on Facebook". People don't really think about social media channels having an end, and so when they do people are often confused. It would be great if there was specific functionality for such things, like automatically turning off comments to all videos etc, but we haven't really worked through the related issues as a society yet so there isn't really a common understanding of what we even want to have happen when people move on. -
MFT has been dead for decades now - everyone who hasn't been living under a rock for the last 10 years knows this. What people don't know is that due to a quirk in quantum physics and the way that time works, MFT was actually dead before it was invented. This means that my GH7 and GX85 and OG BMPCC and BMMCC never existed, don't exist, and when MFT finally "dies" somehow will disappear from my house. I bet you even think the earth is round... some people are just too much!
-
Nice! The other thing to consider when testing ISO and noise in the final image is the delivery part of the pipeline. If I shot in two different modes and then processed them differently in my NLE, I might be able to tell the difference between them in my NLE. But no-one except you is watching your footage in your NLE, so you'll be exporting it, probably to h264 or h265, and you might not be able to tell the difference between them at this point. If you're going to be uploading them to a streaming service, then that service will decompress, process (NR, sharpening, who knows what else) and then brutally re-compress it. Lots of things are visible in the NLE and are completely gone or mangled beyond recognition in the final export or stream.
-
Just make sure you're testing the options in the full image pipeline, so comparing finished 709 grades. So many people only test one part of the pipeline and ignore the rest. I haven't really experimented much with the AF on the GH7 as I'm used to the AF on the GX85 etc, and I tend to use manual lenses in lower light. AF is very difficult to test as well, and @Davide DB has posted before about how lens-dependent it can be too. Maybe there are AF tests online? Playing peekaboo with your camera seems a popular camera reviewer pastime!
-
I'm not sure how this would translate, but my GH7 does far better when I raise the ISO to get a proper exposure in-camera vs shooting under exposed and raising the exposure in post. For some reason the shadows are quite noisy, even at native ISOs. This is shooting in C4K Prores so it's not a codec issue.
-
Just a note to say that it would probably be worth doing some tests ahead of the event. Situations like this involve many variables and most often people don't consider all of them because they don't do any methodical tests. You are assuming that the AF will work differently between different picture profiles, but I would suggest the AF would be operating on the image before the picture profile is applied, so it shouldn't matter... but, once again, you should test this to confirm. Another thing to consider is if you can push the shutter angle to 270 degrees or even 360 degrees. If it's a worship setting then making the footage seem a bit more surreal might be appropriate, and you can get another half or full-stop of exposure this way. You should also test NR in post - it's not ideal but it might give a better result overall considering none of your scenarios are operating in the cameras ideal operating range. I've done a lot of shooting with cameras at/beyond their capabilities and when you're pushing things you're trading off the drawbacks of each strategy.
-
Digital zoom is definitely an underrated feature of these higher resolution cameras. On my GH5 I used the 2x punch-in on my 17.5mm F0.95 to get 35mm and 70mm FOVs, and on my GX85 I used it with the 14mm F2.5 pancake lens to get 31mm and 62mm FOVs in a pocketable form-factor. The crop function on the GH7 is different and a bit more restrictive. You get continuous zooming, but only to the point where the resolution you've chosen is at/near 1:1 crop into the sensor. So, if you've got the 14mm lens on there and you're shooting in C4K, you enable the feature and it pops up a box on the screen saying "14mm" and you can zoom in more and more by pushing or holding a button and it goes from 14 - 15 -16 - 17mm, but it won't let you go further. If you're in 1080p mode then it goes from 14mm to 38mm. Conveniently, if you disable the mode then it goes back to 14mm but if you re-enable it then it goes back to whatever zoom you were at previously, so it's easy to set a zoom level you like and then jump in and out of that FOV. My testing didn't indicate any IQ issues with it, in 24p mode anyway, so I think it's probably downscaling from a full sensor read-out. Not only is it really good for getting more FOVs from primes, but it's also great in extending the long end of your zooms too.
-
My advice is to forget about "accuracy". I've been down the rabbit-hole of calibration and discovered it's actually a mine-field not a rabbit hole, and there's a reason that there are professionals who do this full-time - the tools are structured in a way that deliberately prevents people from being able to do it themselves. But, even more importantly, it doesn't matter. You might get a perfect calibration, but as soon as your image is on any other display in the entire world then it will be wrong, and wrong by far more than you'd think was acceptable. Colourists typically make their clients view the image in the colour studio and refuse to accept colour notes when viewed on any other device, and the ones that do remote work will setup and courier an iPad Pro to the client and then only accept notes from the client when viewed on the device the colourist shipped them. It's not even that the devices out there aren't calibrated, or even that manufacturers now ship things with motion smoothing and other hijinx on by default, it's that even the streaming architecture doesn't all have proper colour management built in so the images transmitted through the wires aren't even tagged and interpreted correctly. Here's an experiment for you. Take your LOG camera and shoot a low-DR scene and a high-DR scene in both LOG and a 709 profile. Use the default 709 colour profile without any modifications. Then in post take the LOG shot and try and match both shots to their respective 709 images manually using only normal grading tools (not plugins or LUTs). Then try and just grade each of the LOG shots to just look nice, using only normal tools. If your high-DR scene involves actually having the sun in-frame, try a bunch of different methods to convert to 709. Manufacturers LUT, film emulation plugins, LUTs in Resolve, CST into other camera spaces and use their manufacturers LUTs etc. Gotcha. I guess the only improvement is to go with more light sources but have them dimmer, or to turn up the light sources and have them further away. The inverse-square law is what is giving you the DR issues. That's like comparing two cars, but one is stuck in first gear. Compare N-RAW with Prores RAW (or at least Prores HQ) on the GH7. I'm not saying it'll be as good, but at least it'll be a logical comparison, and your pipeline will be similar so your grading techniques will be applicable to both and be less of a variable in the equation. People interested in technology are not interested in human perception. Almost everyone interested in "accuracy" will either avoid such a book out of principle, or will die of shock while reading it. The impression that I was left with after I read it was that it's amazing that we can see at all, and that the way we think about the technology (megapixels, sharpness, brightness, saturation, etc) is so far away from how we see that asking "how many megapixels is the human eye" is sort-of like asking "What does loud purple smell like?". Did you get to the chapter about HDR? I thought it was more towards the end, but could be wrong. Yes - the HDR videos on social media look like rubbish and feel like you're staring into the headlights of a car. This is all for completely predictable and explainable reasons.. which are all in the colour book. I mentioned before that the colour pipelines are all broken and don't preserve and interpret the colour space tags on videos properly, but if you think that's bad (which it is) then you'd have a heart attack if you knew how dodgy/patchy/broken it is for HDR colour spaces. I don't know how much you know about the Apple Gamma Shift issue (you spoke about it before but I don't know if you actually understand it deeply enough) but I watched a great ~1hr walk-through of the issue and in the end the conclusion is that because the device doesn't know enough about the viewing conditions under which the video is being watched, the idea of displaying an image with any degree of fidelity is impossible, and the gamma shift issue is a product of that problem. Happy to dig up that video if you're curious. Every other video I've seen on the subject covered less than half of the information involved.